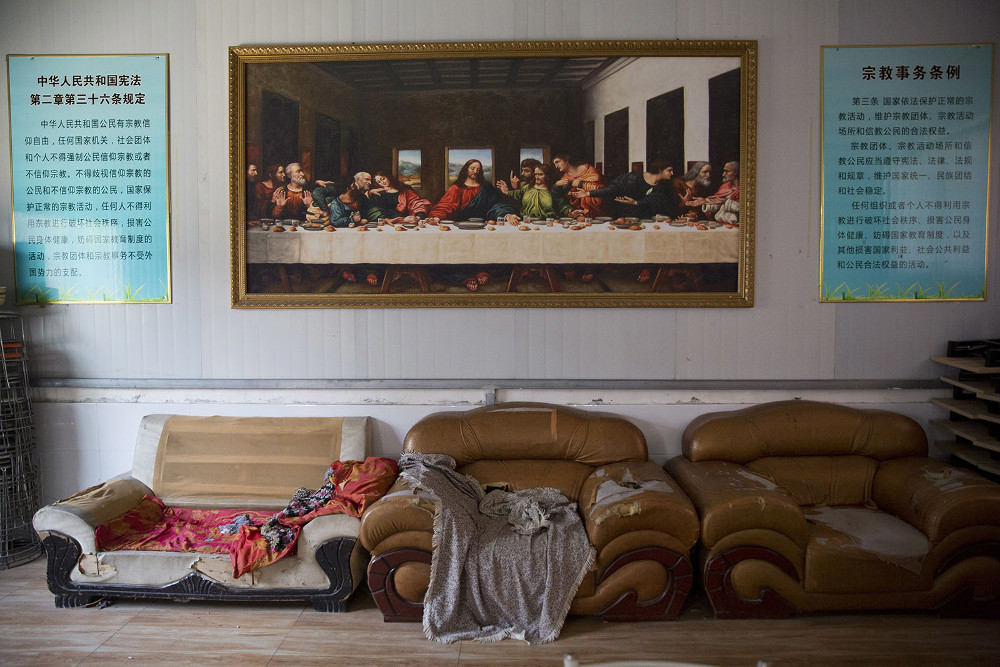
A painting of the Last Supper is seen next to posters quoting China's constitution on religious freedom in a house church shut down by authorities near the city of Nanyang in central China's Henan Province. Under President Xi Jinping, China's most powerful leader since Mao Zedong, believers are seeing their freedoms shrink dramatically even as the country undergoes a religious revival. Experts and activists say that as he consolidates his power, Xi is waging the most severe systematic suppression of Christianity in the country since religious freedom was written into the Chinese constitution in 1982. (AP/Ng Han Guan)
With its particular focus on China's oppression of religion and human rights, an independent watchdog group has decried in its annual report the state of religious freedom across the globe.
The U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom, a bipartisan organization created 20 years ago, concludes in its Monday (April 29) report that "innumerable believers and nonbelievers across the globe continued in 2018 to experience manifold suffering due to their beliefs."
The commission cites dozens of countries in its 234-page report but especially notes China's repression of a range of religious beliefs — including Tibetan Buddhists, Christians, Falun Gong practitioners, Uighur Muslims and human rights defenders.
While the State Department's annual international religious freedom report covers every nation in the world other than the U.S., the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom annually documents fewer than 30 countries that have the most significant religious freedom violations.
The commission recommends that the State Department redesignate the following 10 countries as "countries of particular concern," or CPCs: Burma, China, Eritrea, Iran, North Korea, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan.
The State Department designated these countries as CPCs in November.
The commission thinks six additional countries should be cited as countries of particular concern: Central African Republic, Nigeria, Russia, Syria, Uzbekistan and Vietnam.
The commission adds that it has given 12 other nations its Tier 2 designation for the next most serious level of religious freedom violations: Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cuba, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Laos, Malaysia and Turkey.
In addition, the commission is calling on the State Department to list five nonstate actors, or organizations outside a government's control, as "entities of particular concern": the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS; the Taliban in Afghanistan; al-Shabab in Somalia; Houthis in Yemen; and Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham, or HTS, in Syria.
China, along with Russia and Sudan, has been a focus of the watchdog since 1999 as it prepared to cite religious freedom violators in its first annual report the following year.
Two decades later it notes that Uighur Muslims, in particular, remain severely repressed by Chinese officials.
Advertisement
"Nearly 20 years later, Muslims are constantly surveilled, their phones confiscated and scanned, their skin pricked for blood samples to collect their DNA, their children prohibited from attending mosque," reads the report's introduction. "Even worse, the Chinese government has ripped entire families apart, detaining between 800,000 and two million adults in concentration camps and relegating some of their children to orphanages."
The commission calls for the U.S. government and others across the globe to sanction Chinese agencies and officials for their role in serious religious freedom violations and to set Uighur and other Muslims free. It also calls for the release of prisoners of conscience, including Muslims, Buddhists and Christians.
Other countries beyond China are also highlighted, including Vietnam, Sudan and Tajikistan, which the report says are suppressing religious freedom and permitting persecution. The commission cites Eritrea and Russia along with China as examples of countries that brand religious minorities as "extremists."
"In 2018, both state and nonstate actors increasingly used religion as a tool of exclusion to isolate, marginalize, and punish the 'other' through discrimination and violence," the report states, citing blasphemy laws in Saudi Arabia and Pakistan as examples.
The report notes religious freedom successes — including the release of Pastor Andrew Brunson, an American evangelical, from a Turkish prison — and continuing challenges for the Trump administration.
"Longstanding flaws in the U.S. government's processing of asylum-seekers at ports of entry and the border remained unaddressed," it says.
The commission recommends that the administration appoint a special adviser on international religious freedom to the staff of the National Security Council. It also seeks an increase in the use of sanctions to target government officials, military units and agencies that are severe religious freedom violators. And the Commission for International Religious Freedom requests that the U.S. Agency for International Development and the State Department assist countries in providing textbooks and other training materials that describe religious groups accurately.
The report, issued after recent attacks on mosques in New Zealand and churches in Sri Lanka, also calls for the administration to set aside money for the State and Defense departments "to train and equip local officials and communities to protect places of worship and other holy sites, especially in countries where such sites face a high risk of attack."